Spherical building-screen "Sphere" opened in Las Vegas. The world's largest futuristic building in the form of a sphere covered with LED panels is open in Las Vegas. The screen of the unusual building "MSG Sphere" is made of 1.2 million LED panels, the display area is 54,000 sq.m. it is now the largest LED display in the world. There is also a spherical screen inside the building of the sphere, its resolution is 19,000 by 13,500 pixels, 164,000 speakers are installed inside the hemisphere. Thanks to such a large number of LEDs, at night the building is very brightly lit from the outside, and it can be seen even during the day for several kilometers. The MSG Sphere building has a capacity of 17,600 seats or 20,000 standing places and will host major concerts and sporting events. MSG Sphere will officially open on September 29th. The project of an unusual building cost 2.3 billion dollars, and is now considered the most expensive entertainment venue in Las Vegas.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
News of science and technology around the world
- Thread starter Soldier35
- Start date
An image of the Jezero Crater on Mars taken by NASA’s Perseverance Mars Rover has found potential signatures for organic molecules on the planet, which could be evidence for the presence of key building blocks of life there. The signatures found point to a class of carbon-based molecules that could have been left behind by ancient microbial life.

 indianexpress.com
indianexpress.com
Anyone wonders , how much impact ll it have on how human beings perceive the universe and life even if a microbial life form is discovered in some planet .. Evidence of microbial life form ll force people to believe , there is more as we are only able to see a dust in a unknown massive dune expanding at the light of speed .

Perseverance rover may have found key building blocks of life on Mars
NASA's Perseverance Mars Rover may have found organic chemicals that are important building blocks of life.
Anyone wonders , how much impact ll it have on how human beings perceive the universe and life even if a microbial life form is discovered in some planet .. Evidence of microbial life form ll force people to believe , there is more as we are only able to see a dust in a unknown massive dune expanding at the light of speed .
Researchers from South Korea, state the creation of a material known as LK-99 that can conduct superconductivity at room temperatures.

 www.indiatoday.in
www.indiatoday.in

What is LK-99, the 'magical' superconductor that could change the world
Two new papers uploaded to the arXiv preprint server, by researchers from South Korea, state the creation of a material known as LK-99 that can conduct superconductivity at room temperatures.
Sending Russia's Luna-25 station to the Moon and mission objectives. The Russian Soyuz-2.1B rocket with the Luna-25 automatic station launched today at 02:10 am Moscow time from pad 1C of the Vostochny cosmodrome. We can say that this is a historic moment, since this is the first launch of a Soyuz rocket with a Russian lunar lander in 47 years. The carrier rocket has worked in the normal mode, the upper stage has separated from the third stage of the rocket and is currently putting the automatic station on a flight trajectory to the Moon. The flight to the Moon will take about 5 days, during which time there will be two trajectory corrections: the first - 1.5 days after launch, the second - a day before entering orbit around the Moon. After performing the calculations, a soft landing should occur for the first time in the world in the region of the South Pole of the Moon. Tentatively this will happen on August 21st. The station will conduct a whole range of studies - first of all, the search for water. If successful, the prospect of building a lunar base and industrial use of the satellite opens up. The station will take lunar soil for one year, study it and transmit data to the ground. In 2027, Russia should launch the Luna-26 station, in 2028 - Luna-27, and sometime after 2030 - Luna-28. These four missions will be the first phase. After that, Russia, together with China, will move on to the next phase - the possibility of a manned visit to the moon and the construction of a lunar base. At the same time, the Indian spacecraft Chandrayan-3 is heading towards the Moon. Both missions are aimed at the little-studied South Pole of the Moon.
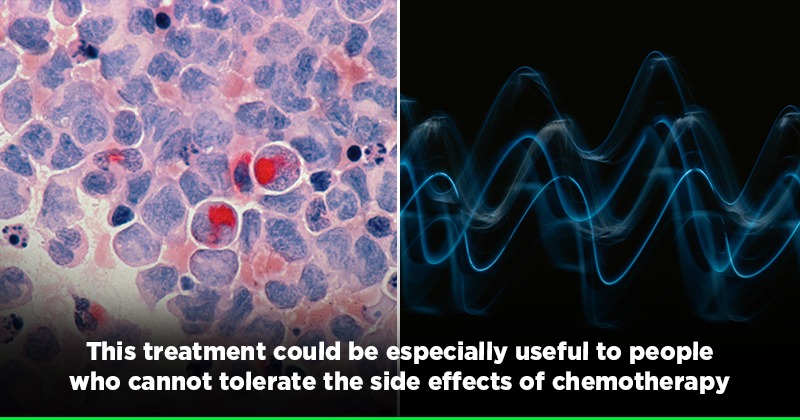
Researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a sound technology can get rid of cancer tumours and help with treatment.
 www.indiatimes.com
www.indiatimes.com

Researchers Use Sound Waves To Target And Destroy Cancer Tumours
The technique operates through sound waves that can help with the physical destruction of cancerous tumours. Owing to the breakdown of cells walls, doctors could also detect tumours that couldn't be found earlier.
Pilot robot PIBOT can replace pilots. As you know, automation and robotization are gradually reducing the number of workers, it would seem that this will not affect the pilots so quickly, but progress has also affected them. South Korean Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) engineers and researchers have created the first robotic aircraft pilot. The PIBOT pilot robot controls the aircraft with its own hands, while it is not known whether it can replace the pilots, but the robot is quite well done. The humanoid robot uses data from the sensors of the aircraft, and what he sees himself with the help of the camera. The creators claim that in some areas it even surpasses a person - for example, it holds the plane more evenly during takeoff and landing. The robot is able to read and memorize flight charts and emergency protocols, while quickly responding to emergencies. Unlike other systems, the robot does not require modification of the aircraft - it can control any aircraft. The robot can already control all the operations of the simulator aircraft, such as taxiing, takeoff, landing and flight. The project is expected to be fully developed in 2026.
UK's Vulcan laser set for £85M upgrade to 20PW output
Central Laser Facility funding is expected to deliver the world's most powerful laser pulses.
Heavy Duty Robot Figure-01 shown in USA. The American startup Figure showed the first video of its robot Figure 01 walking, which will have to replace people when performing heavy mechanical work. The company was able to attract $70 million in investments into the project in just a year. The company's founder, Brett Adcock, recruited professionals from companies such as Boston Dynamics, Google Deepmind, Tesla and Apple. Figure, a humanoid robot, is designed to perform simple tasks in a warehouse, such as moving items. However, over time its functionality will expand. Now the 168-centimeter Figure robot is already capable of carrying loads weighing up to 20 kg. To train the robot to become a loader, the company even built a warehouse.
The first flight of the Russian long-haul passenger aircraft Il-96-400M took place. The flight of the prototype aircraft took place at an altitude of up to 2000 meters, at a speed of up to 390 km/h and lasted 26 minutes. The aircraft can accommodate up to 370 passengers, and the new navigation system is created from Russian components taking into account current international requirements. The aircraft is a modernized version of the Il-96-300, features a fuselage lengthened by 9.35 meters and is equipped with more powerful Russian PS-90A1 engines. The aircraft may have a cargo configuration. The maximum flight range of the Il-96-400M in a two-class passenger configuration is 8.1 thousand km. During the first flight, stability, controllability, systems, and radio equipment were checked.
The Aeromax company announced the launch of production of a new model of the Russian unmanned cargo helicopter SH-3000. The SH-3000 helicopter-type drone was developed very quickly, its development began a year ago. The first prototypes of the helicopter will appear in 2024 and testing will begin then. So far, only civilian versions of drones have been reported. The SH-3000 drone is adapted for flights in difficult weather conditions. The length of the helicopter is about 13 meters. Its maximum speed reaches 210 km/h. The drone is capable of staying in the air for up to five hours and covering a distance of up to 900 km. The cargo drone is designed to transport cargo weighing up to 1000 kilograms. It is planned to use the helicopter in hard-to-reach regions of Russia.
Serial production of Russian UAVs from the Flying Machines of Thuring company from Moscow will begin in Kaluga. The launch of production will take place at the Kaluga Electromechanical Plant. The drones promise two and three times redundancy of all systems, 5 times redundancy of communication channels, and 360-degree video streaming for the pilot. Two aircraft-type UAVs with vertical takeoff and landing will be produced, the T-300 UAV and the TFM-15 UAV. The drones are based on a scalable and easily upgradeable platform. The company's drones are designed primarily for logistics purposes, but drones can be used in other areas: from monitoring to agriculture. Modernization for military functions is also possible. Regarding the characteristics, the TFM-15 UAV has a payload of 15 kg and a flight speed of up to 130 km/h, the standard version has a flight range of 200 km, but there is a hybrid version with an engine-generator that can fly up to 800 kilometers. The T-300 UAV is designed for transporting heavy loads, its payload capacity is up to 130 kg, the flight range is the same 200 km, in a hybrid version up to 1000 km. The company has been carrying out import substitution of components for its UAVs since 2021.
The Russian company Geoksan has begun serial production of the Geoscan 801 drone. The Geoscan 801 compact quadcopter is equipped with a thermal imager with a resolution of 640 by 512 and a camera with 14x magnification. The drone records video in 4K format and transmits it over a distance of up to 10 km thanks to a special noise-resistant receiver. The drone is equipped with a cooling system for electronics and heating the battery, so it can fly in any weather, -20 to +40 °C. The drone can be used for a variety of purposes, from entertainment to reconnaissance. For now, the drone is more expensive than its foreign counterparts, but as production increases, the price should drop; there are already orders for the first batch of drones. The drone weighs 1.5 kilograms, flight time is up to 40 minutes, at an altitude of up to 4000 meters. The elemental part of the drone is partly foreign-made.
Iran launched a Salman rocket with a biocapsule inside. This launch is part of Iran's space program to send humans into space. The capsule weighed about 500 kilograms and was launched to an altitude of 130 kilometers; it was equipped with the necessary equipment to study the conditions of human beings in space. Iran did not disclose which animal was in the biocapsule and imitated the astronaut. Previously, 10 years ago, Iran sent two monkeys into space in a biocapsule.
The Russian manufacturer ODK-Aviadvigatel showed what the PD-14 aircraft engine consists of. The PD-14 aircraft engine is the first in the history of modern Russia to have its own certified engine for civil aviation, created taking into account international standards and requirements. In terms of the scale of technical, technological, economic, and marketing problems in the field of aircraft engine building, the creation of the PD-14 engine has become the most ambitious project in Russia over the past 30 years.
Currently, only four countries - Great Britain, Russia, the USA and France - possess the technologies for the full cycle of creating modern turbojet engines.
The first ground tests of the PD-14 took place in 2012, the first flight tests in 2015. In January 2020, the PD-14 underwent additional tests to comply with new international standards for smoke and non-volatile particle emissions. New high-strength Russian titanium and nickel alloys were used to create the engine. The engine nacelle structure consists of 65% composite polymer materials
In total, about 20 new Russian materials were used in PD-14. It is expected that the operating costs of PD-14 engines will be 14-17% lower than those of existing similar engines, and the life cycle cost will be 15-20% lower. The PD-14 engine was developed for the promising Russian airliner MS-21-310. The first flight of MS-21-310 with PD-14 engines took place on December 15, 2020 at the airfield of the Irkutsk Aviation Plant. Today the aircraft continues to fly as part of certification tests. The MC-21 aircraft will replace its competitors Airbus A320 and Boeing 737-800 in Russian airlines.
Currently, only four countries - Great Britain, Russia, the USA and France - possess the technologies for the full cycle of creating modern turbojet engines.
The first ground tests of the PD-14 took place in 2012, the first flight tests in 2015. In January 2020, the PD-14 underwent additional tests to comply with new international standards for smoke and non-volatile particle emissions. New high-strength Russian titanium and nickel alloys were used to create the engine. The engine nacelle structure consists of 65% composite polymer materials
In total, about 20 new Russian materials were used in PD-14. It is expected that the operating costs of PD-14 engines will be 14-17% lower than those of existing similar engines, and the life cycle cost will be 15-20% lower. The PD-14 engine was developed for the promising Russian airliner MS-21-310. The first flight of MS-21-310 with PD-14 engines took place on December 15, 2020 at the airfield of the Irkutsk Aviation Plant. Today the aircraft continues to fly as part of certification tests. The MC-21 aircraft will replace its competitors Airbus A320 and Boeing 737-800 in Russian airlines.
Tests of the MS-21 Russian aircraft, emergency evacuation of passengers. The first all-Russian aircraft MS-21 received approval to carry the maximum number of passengers. To obtain a certificate of approval from Rosaviatsi, the aircraft was tested for emergency evacuation of passengers. Previously, the MC-21 aircraft was allowed to carry no more than 175 people, but tests of emergency equipment showed that it complies with all aviation safety standards and can carry up to 211 passengers. As a result of training tests, it was possible to carry out an emergency evacuation of aircraft passengers faster than 90 seconds, which are provided for by aviation safety standards. The actual evacuation time was 81 seconds. The tests were carried out on an aircraft with the most dense passenger compartment layout. 211 passengers, as well as crew members, 3 pilots and 5 flight attendants were successfully evacuated from the plane. In accordance with the requirements of airworthiness standards, emergency evacuation tests from the aircraft were carried out in conditions as close as possible to the most severe. The evacuation was carried out in the dark, and only half of the aircraft's available emergency exits were used.
In Russia, Tu-214 passenger aircraft are being returned to service. Red Wings Airlines received the first Tu-214 from the Kazan aircraft plant. It is worth noting that the aircraft with tail number RA-64518 was produced in 2009 at the Kazan aircraft plant. It was used first by Transaero for its flights, and then by its current owner, Red Wings. At the end of 2017, it was decided to put the aircraft into storage “due to the acquisition of more profitable aircraft to operate” - the Airbus A321. For the airline, maintaining the Airbus was more economical, because fuel consumption was lower, and the crew consisted of only two people. The return to service of the Tu-214 aircraft is a temporary solution until the production of completely Russian Superjet 100, MC-21-310RUS and Tu-214 is established; it still uses 13% of imported spare parts. The process of replacing spare parts with Russian analogues is underway, but this may take several years.
The all-Russian freight mainline electric locomotive 3ES8 "Malachite" from the Ural Lokomotiv company set off on its first voyage. The electric locomotive delivered a train of 77 cars weighing 7018 tons from the Vologda region to the Leningrad region. All main components of the 3ES8 electric locomotive, including the asynchronous traction drive, power equipment and intelligent control systems, were developed and manufactured in Russia. The carrying capacity of the Malachite electric locomotive is 42% higher than that of the previous generation locomotives. It can drive trains of cars weighing over 7 thousand tons and up to 1 km long in mountainous terrain, and up to 9 thousand tons on flat terrain. The 3ES8 Malachite electric locomotive will become the base platform for a line of promising Russian locomotives. The 3ES8 electric locomotive in its main characteristics is not only not inferior to the best world models, but also surpasses them in some parameters.
The electric locomotive 3ES8 "Malachite" is equipped with ATD1000 engines with a power of 1000 kW, the design speed of the electric locomotive is 120 km/h.
The electric locomotive 3ES8 "Malachite" is equipped with ATD1000 engines with a power of 1000 kW, the design speed of the electric locomotive is 120 km/h.
The Russian Ka-226T transformable helicopter took off for the first time in Kolyma. One of the main advantages of the Ka-226T helicopter is its modular design. In 30 minutes, the helicopter can be converted into a passenger, cargo, ambulance, search and rescue and police version by replacing one module with another. The helicopter is resistant to side winds and has a high rate of climb; the coaxial design ensures compactness and high maneuverability. The helicopter continues to be improved; work is underway on a new modification of the Ka-226T helicopter, with the replacement of French Arrius 2G1 engines with more powerful Russian VK-650V engines. The cruising speed of the Ka-226T helicopter is 190 km/h, the rate of climb is 12.5 m/s, the flight altitude is up to 6100 meters, and the range is up to 475 km. Maximum take-off weight is 3600 kg, payload in the transport cabin is 785 kg. The helicopter can be operated by one to two pilots and can carry up to seven people.
